Fuel instability often occurs when the aromatic solvency of the fuel is disturbed, typically by paraffinic solvents used as cutter stocks, or fuels based on paraffinic crudes.
Bunkers from different fuel sources may separately pass ISO 8217 certification tests, yet when blended and subjected to age and heat on board the vessel, the bunkers become incompatible. Heavy sludge affects the fuel system, causing increased maintenance costs and operational problems.
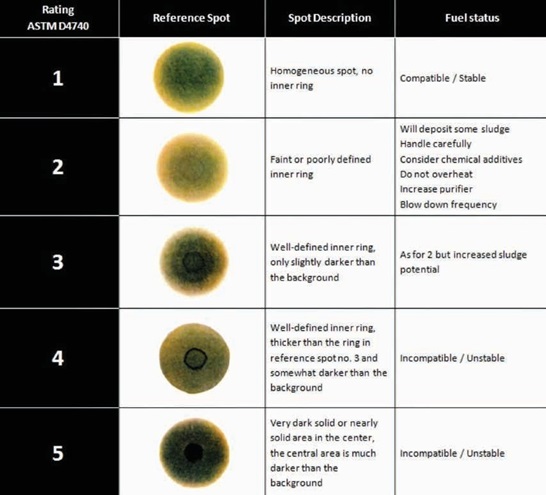
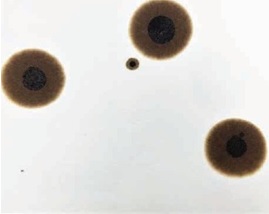
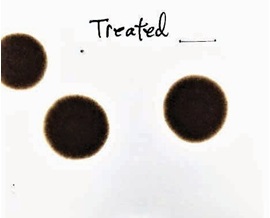
ASTM D 4740 measures fuel compatibility and resistance of mixed fuels to form sludge under a ship’s high-temperature fuel handling conditions. Demonstrated in this test by Intertek Caleb Brett laboratory in California, USA, a mixture of 3.5% sulphur HFO 380 bunker samples that were initially ISO 8217 compliant, but when aged and mixed, became highly unstable.